Powerful Artificial Intelligence engines like Chat GPT4 and Midjourney v5 are quickly moving into the mainstream. This 3-part series on the expanding prevalence of Artificial Intelligence (A.I.) will consider the topic with respect to art and the creative economies in our region and beyond. In this opening segment, Taliesin Thomas PhD explores the basic definitions of A.I. and where the current conversation is moving.

Photo Credit: Taliesin Thomas
The noticeable buzz surrounding Artificial Intelligence (A.I.) appears to be infiltrating nearly every category of contemporary culture, especially creative fields. What exactly is A.I. and how does it work? What are the implications of A.I. for art? Although art made with semi-autonomous machines has been around since the 1960s, we are in an entirely new era of technological realities. First let us consider the pairing of these two words: ‘artificial’ and ‘intelligence.’ These concepts inspire distinct questions surrounding A.I. and its rising significance in our increasingly interconnected society. The term ‘artificial’ presents a wary definition to start—synonyms include ‘bogus’, ‘counterfeit,’ ‘factitious,’ and ‘faked.’ This provokes a circumspect context from the outset of the conversation: can we trust this fabricated form of perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information? Second, the notion of ‘intelligence’ is arguably the basis of our entire civilization. We endure and increase our collective agency as a species thanks to our combined intelligence. Intelligence can be defined in various ways, including the capacity for understanding, self-awareness, reasoning, planning, critical thinking, and creativity. The power of our singular human experience is precisely our ability to cultivate intellect throughout our life journey.

Image credit: Taliesin Thomas
Thus, we proceed with a sense of discernment regarding A.I. as a ‘phony mind’ yet we must marvel at its swift development and implementation in various realms of society, notably commercial applications. A.I. systems function through a foundation of specific hardware and software tools that consume large quantities of organized data that—through processing techniques—produce specific algorithms or patterns. Those algorithms in turn provide computing devices with step-by-step instructions for how to complete a specific task and can be manipulated to ‘create’ or output in distinct ways. A.I. is now employed for a variety of purposes including expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, and machine vision. The ride service Uber, for example, utilizes sophisticated A.I. machine learning algorithms to predict when people are likely to need rides in certain areas, which helps proactively get drivers on the road and to where they are needed most.
As a novel technology, A.I. is being progressively employed within the creative sector as well, often in fascinating ways. I anticipated the A.I. generated voice for Andy Warhol as encountered in the Andy Warhol Dairies would sound gimmicky and bizarre, however, I was delighted by the opposite effect. Not only does the Warhol’s voice sound incredibly accurate, but it also brings to life his articulate mind (and heart) in a beautiful and believable manner. We already know Warhol as an icon extraordinaire and enduring face of Pop Art, but this intimate series reveals Warhol the lover, and his words are pulled straight from his personal dairies and personified through A.I. technology. The result is a dreamy and eloquent Warhol voice, and it reduced me to bouts of sobbing throughout the series (the emotional quality is undeniable). The company Resemble AI crafted Warhol’s A.I. voice with just 3 minutes and 12 seconds of usable data in the form of existing audio recordings. The Andy Warhol Dairies is a marvelous example that demonstrates the success of A.I. as a tool that brings ever greater insight to the art of our times—and in the case of Warhol, a deceased artist who remains timeless.

Image credit: Taliesin Thomas
The pressing question in all of this seems to be: how does A.I. impact our concept of intelligence and creativity and our ‘ownership’ of that very intelligence and creativity? In other words, to restate a familiar concern about the expanding role of technology and the human mind in all its formats since the first publication of Mary Shelly’s Frankenstein (1818) and the dawn of the computing age: can machines ‘think’ for us? In the meantime, critics such as New York based arts, culture and technology writer Mike Pepi propose: “These so-called ‘creative’ machines are limited in that they can only ever remix existing media and data, they cannot truly create anything new. This is the province of human ingenuity alone.” Artists, fear not! These fictitious A.I. minds are mere derivative producing hacks! In any case, the fundamental thing to understand about A.I. is that it is as a unique form of simulated intelligence by way of computer systems that aim to assist humans achieve in increased capacities. Here one must acknowledge that notions of ‘human’ increasingly point toward the ‘posthuman’ in our hyper-stimulated digital era. A recent article at The Verge highlights the issues around copyright laws and exposes the ruffle between Getty Images and A.I. generated visions of humans that are downright freakish. Indeed, these are dense conceptual paradigms transforming our planet in real-time.
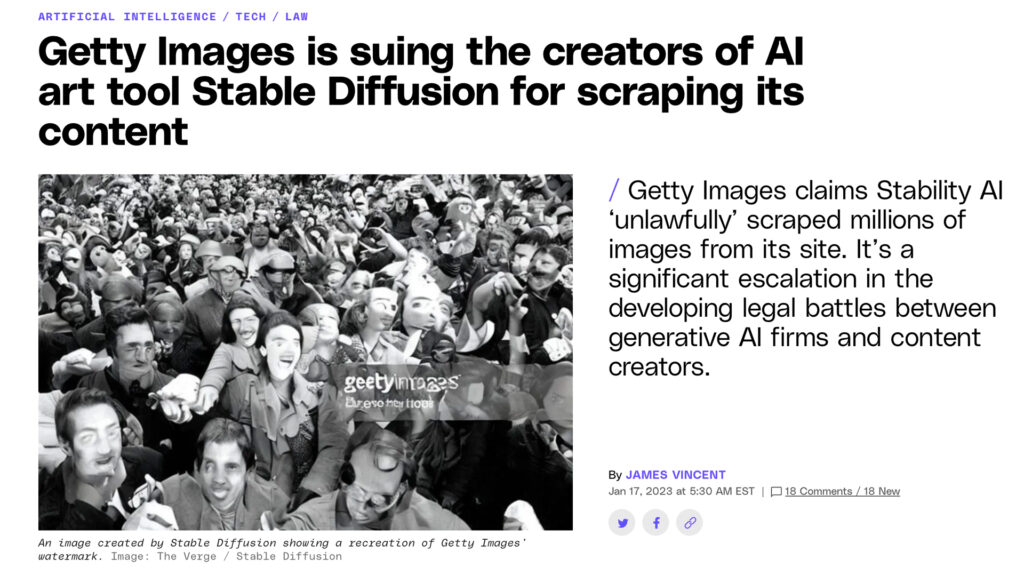
Nevertheless, A.I. is here to stay, so we must embrace it as part of the evolving global reality of today. We also recognize, however, an underlying apprehension for creatives, since corporate driven A.I image generators pose a threat to their livelihood. According to a recent article published by Artnews, the latest advancements in machine-learning programs have transformed A.I. into an impressive creative tool that seems capable of outpacing—and underpricing—human artists, sparking a real concern in diverse creative circles. Anxieties surrounding A.I. and art are highest among graphic artists and commercial illustrators, whose very livelihood is based on their ability to design artistic content specific to a clients’ vision. Another Artnews piece also warns that A.I. systems ‘learn’ by sifting through numerous man-made images that are often scraped from online sources by tech companies and often without the consent of their authors. As stated by writer Taylor Dafoe: “A.I. advocates argue that this practice is protected by fair use laws; artists have said it violates their copyrights.” How will A.I.’s artistic capabilities intimidate even more areas within the wider creative field?

Image Credit: Taliesin Thomas
I agree with sceptics who suggest that the vast realm of art practices and material embodiments of aesthetic culture will not be undermined by the new A.I. landscape. And I agree with critical thinkers such as Mathew Dryhurst who states: “I do not believe that artists are in too much danger of being replaced by A.I. Artistic practices are so much more complex than a style that can be mimicked. What we value of art is more social than we often acknowledge.” Other cultural commentators such as Martin Herbert get to the heart of the matter from a meta perspective. In his recent article “I’m an Art Critic. Will AI Steal My Job?” he states the obvious regarding the entire A.I. project: “At the base of this inhuman ‘creativity’, of course, is human labour.” He also makes an important point about the ‘real’ value of art as a matter of ‘real’ lives lived: “The contemporary art scene seems, almost nostalgically, tied to people: artists, as fronting personalities and aspiration models, seem as important as the art.” Undoubtedly it is the corporeal, messy, compelling narratives of artists and their art—the true blood and guts of a creative life—that give art its enduring allure. Thus, we can welcome A.I. onto the scene as fellow ‘counterfeit’ creative as we remain rooted in a pulsating world of manifestation that comes into being precisely through authentic being.
In the next installment (II of III), we will hear from regional professionals who amplify our perspective on A.I. and its significance in arts fields especially.
Taliesin Thomas, Ph.D. is an artist-philosopher, writer, lecturer, and collector based in Troy, NY. Since 2007, she is the founding director of AW Asia and the collection manager of Art Issue Editions—two private art collections based in New York that are the foundation for collaborations and projects with artists and museums
worldwide. Thomas has lectured and published widely on contemporary art. She is the director of the Critical Forum program at the Arts Center for the Capital Region, NY and she is a faculty member at School of Visual Arts, NY. Thomas studied studio art, aesthetics, theory, and philosophy at Bennington College, Columbia University, and The Institute for Doctoral Studies in the Visual Arts.







